cfds and spreadbets are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 68% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Inflation Beating Stocks
Introduction
As the market spectre of rising inflation has come back to the fore, we look at what it is and which sectors can offer investors a shelter from it. The inflationary concerns rearing up at the moment are on a global level and fuelled by several catalysts including, a hangover from the lack of economic activity during the pandemic, China’s current lockdowns and impact on supply chains, and the conflict in the Ukraine.
If rapid inflation does set in, some product and service sectors can pass inflation on to their customers a bit easier than others in the form of a price increase. A lot of utilities can do so, as their pricing agreements with regulators tie price increases to the inflation rate. Vice stocks also offer inflationary covers largely due to the fact their consumers will continue to consume regardless of prices. This includes tobacco, gambling and alcohol stocks. Tobacco and alcohol companies have a lot of pricing power because consumers crave their products.
Luxury brand’s also offer a form of defence against inflation as the purchasing power of the luxury brand consumer doesn’t usually get dented quite as much as the spending power of the average man on the street. However you will note we don’t highlight any luxury brands in the report and that’s because whilst they can offer a hedge against inflation, they also have large exposure to China and the Asian markets and so with a lot of Covid, supply chain and growth concerns in China they may not be quite as defensive as they had been in the past.
Commodity stocks can also offer a shelter as the price of the underlying commodities tend to increase; this is even more prominent in the recent markets as talk of the beginning of a commodities super cycle is being banded around (but that’s more of a topic for another report).
The final sector that can offer a shelter is defence stocks, whilst not the top of everyone’s list the contracts they win are with government bodies so avoid the knock on from consumer’s drop in buying power. The defence sector has also been under pressure for years especially in the UK as the government spending on defence has been weak for years, of course in the current climate this is changing.
What is Inflation, and what does it mean.
Inflation is the decline of purchasing power of a defined currency over a set period. This can be reflected in the increase of an average price of a basket of selected goods and services in an economy over a defined period. The rise in the general level of prices, often expressed as a percentage, means that a unit of currency effectively buys less than it did previously.
The basket (more commonly known as price indexes) generally includes the following mix:- commodities like metal and fuel, food grains, utilities, and services like healthcare and entertainment. Inflation aims to measure the overall impact of price changes for a diversified set of products and services and allows for a single value representation of the increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
Types of Price Indexes
The two key price indexes are The Consumer Price Index and the Wholesale price index:-
The Consumer Price Index
The CPI is a measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of goods and services which are of primary consumer needs. They include transportation, food, and medical care. CPI is calculated by taking price changes for each item in the predetermined basket of goods and averaging them based on their relative weight in the whole basket. The prices in consideration are the retail prices of each item, as available for purchase by the individual citizens. Changes in the CPI are used to assess price changes associated with the cost of living, making it one of the most frequently used statistics for identifying periods of inflation or deflation.
The Wholesale Price Index
The WPI is another popular measure of inflation, which measures and tracks the changes in the price of goods in the stages before the retail level at the wholesale level. While WPI items vary from one country to other, they mostly include items at the producer or wholesale level. For example, it includes cotton prices for raw cotton, cotton yarn, cotton gray goods, and cotton clothing. Although many countries and organizations use WPI, many other countries use a similar variant called the producer price index (PPI).
Impact on Cash and Bonds
Whichever way you look at it, inflation is not good for cash. Money kept under the mattress will find its value eroded as prices rise and with it near impossible to find a savings account offering an inflation beating (or even equalling) interest rate, money held in a bank account could and probably will suffer. Inflation is not really that positive for bonds either. If prices rise at a rate greater than the interest you earn on a bond, you’ll find the value of your fixed income fall in real terms. Consider a five-year bond paying 2% nominal interest. If inflation rises to 2.5% for those five years, your bond won’t be able to keep up.
Causes of Inflation
An increase in the supply of money is one of the key root causes of inflation, though this can play out through different mechanisms in the underlying economy. Money supply can be increased by the monetary authorities either by printing and giving away more money to the individuals, by legally devaluing (reducing the value of) the legal tender currency, more (most commonly) by loaning new money into existence as reserve account credits through the banking system by purchasing government bonds from banks on the secondary market (Quantitive easing). In all instances of money supply increase, the money loses its purchasing power. The mechanisms of how this drives inflation can be classified into three types: Demand-Pull inflation, Cost-Push inflation, and Built-In inflation.
Types of Inflation
Demand-Pull Effect
Demand-pull inflation occurs when an increase in the supply of money and credit stimulates overall demand for goods and services in an economy to increase more rapidly than the economy's production capacity. This increases demand and leads to price rises. With more money available to individuals, positive consumer sentiment leads to higher spending, and this increased demand pulls prices higher. It creates a demand-supply gap with higher demand and less flexible supply, which results in higher prices.
Cost-Push Effect
Cost-push inflation is a result of the increase in prices working through the production process inputs. When additions to the supply of money and credit are channelled into commodity or other asset markets and especially when this is accompanied by a negative economic shock to the supply of key commodity, costs for all kind of intermediate goods rise. These developments lead to higher cost for the finished product or service and work their way into rising consumer prices. For instance, when an expansion of the money supply creates a speculative boom in oil prices the cost of energy of all sorts of uses can rise and contribute rising consumer prices, which is reflected in various measures of inflation.
Built-In Inflation
Built-in inflation is related to adaptive expectations, the idea that people expect current inflation rates to continue in the future. As the price of goods and services rises, workers and others come to expect that they will continue to rise in the future at a similar rate and demand more costs/wages to maintain their standard of living. Their increased wages result in higher cost of goods and services, and this wage-price spiral continues as one factor induces the other and vice-versa.
Stocks to Watch
British American Tobacco
British American Tobacco plc is a British multi-national company that manufactures and sells cigarettes, tobacco and other nicotine products. The company was established in 1902 with headquarters in London. They have operations in around 180 countries, and its cigarette brands include Dunhill, Kent, Lucky Strike, Pall Mall and Rothmans. Its new age brands also include Vype, Vuse and Glo. Cigarette smoking itself has of course been in decline for years, but there are still an estimated 1.1bn smokers worldwide. Europe has 112mn of them. Cigarette demand is what economists call "inelastic," meaning smokers aren't price sensitive.
Despite a constant barrage of regulation changes and a traditional industry in decline you’d be forgiven for thinking the long-term outlook for tobacco companies is bleak! The reality is the tobacco sector still has a lot going for it and are still making inroads into new world vaping products. The sector has always been appealing with the income investors as well due to the large yields on offer. Recent figures have highlighted BAT’s is still in rude health despite the backdrop.
Key Fundamentals
| Valuation | Balance Sheet | Income Statement |
| Market Capitalization74.972B | Current Ratio (MRQ)0.8457 | Basic EPS (FY)2.9685 |
| Enterprise Value/EBITDA (TTM)8.2470 | Debt to Equity Ratio (MRQ)0.5816 | Basic EPS (TTM)2.9676 |
| Total Shares Outstanding (MRQ)2.27B | Net Debt (MRQ)35.933B | EPS Diluted (FY)2.9556 |
| Number of Shareholders108.467K | Total Debt (MRQ)39.198B | Net Income (FY)6.789B |
| Price to Earnings Ratio (TTM)11.1881 | Total Assets (MRQ)137.365B | EBITDA (TTM)11.608B |
| Price to Revenue Ratio (TTM)2.9585 | Dividends | Gross Profit (FY)17.819B |
| Price to Book (FY)1.1277 | Dividends Paid (FY)−4.904B | Last Year Revenue (FY)25.713B |
| Price to Sales (FY)2.9540 | Dividend Yield Forward6.5870 | Total Revenue (FY)25.713B |
| Dividends per Share (FY)2.7225 | Free Cash Flow (TTM)7.744B |
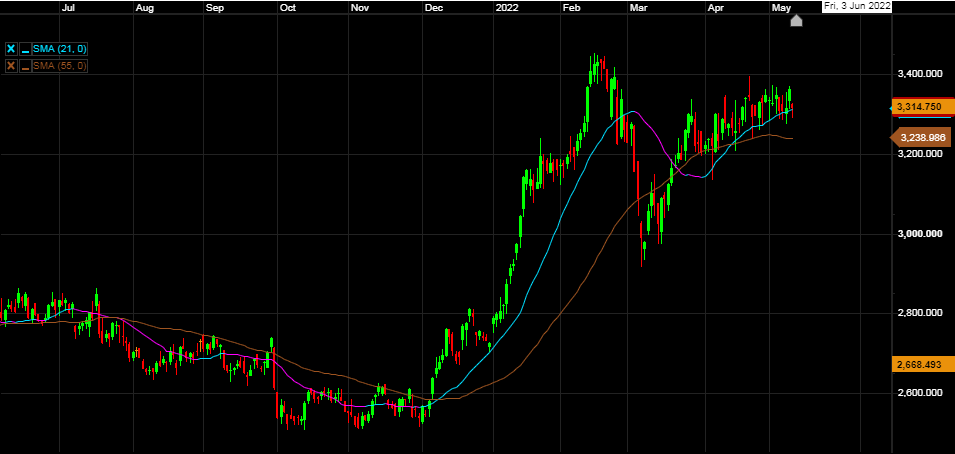
BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh largest in the world based on 2021 revenues. The company manufactures military aircraft, surface ships, submarines and radar systems. Its largest operations are in the UK and US, where BAE Systems Inc are one of the six largest suppliers to the US Department of Defence. Other major markets include Australia, Canada, India, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Qatar, Oman and Sweden, where Saudi Arabia is regularly among its top three sources of revenue.
Defence companies are generally protected from inflation by contracts that allow them to pass on most cost increases to customers. Recently the UK Government decided to increase the defence budget over the next four years after years of reduced spending. With the end consumer for defence stocks being governments there is also very little chance of a drop in activity so again offering a shelter from inflation.
Key Fundamentals
| Valuation | Balance Sheet | Income Statement |
| Market Capitalization23.443B | Current Ratio (MRQ)1.0140 | Basic EPS (FY)0.5516 |
| Enterprise Value/EBITDA (TTM)8.2318 | Debt to Equity Ratio (MRQ)0.8289 | Basic EPS (TTM)0.5516 |
| Total Shares Outstanding (MRQ)3.156B | Net Debt (MRQ)3.245B | EPS Diluted (FY)0.5475 |
| Number of Employees82K | Total Debt (MRQ)6.356B | Net Income (FY)1.758B |
| Number of Shareholders95.7K | Total Assets (MRQ)27.135B | EBITDA (TTM)2.498B |
| Price to Earnings Ratio (TTM)13.5938 | Dividends | Gross Profit (FY)5.192B |
| Price to Revenue Ratio (TTM)1.2202 | Dividends Paid (FY)−777M | Last Year Revenue (FY)19.521B |
| Price to Book (FY)3.1631 | Dividend Yield Forward3.3655 | Total Revenue (FY)19.521B |
| Price to Sales (FY)1.2242 | Dividends per Share (FY)0.2510 | Free Cash Flow (TTM)1.914B |
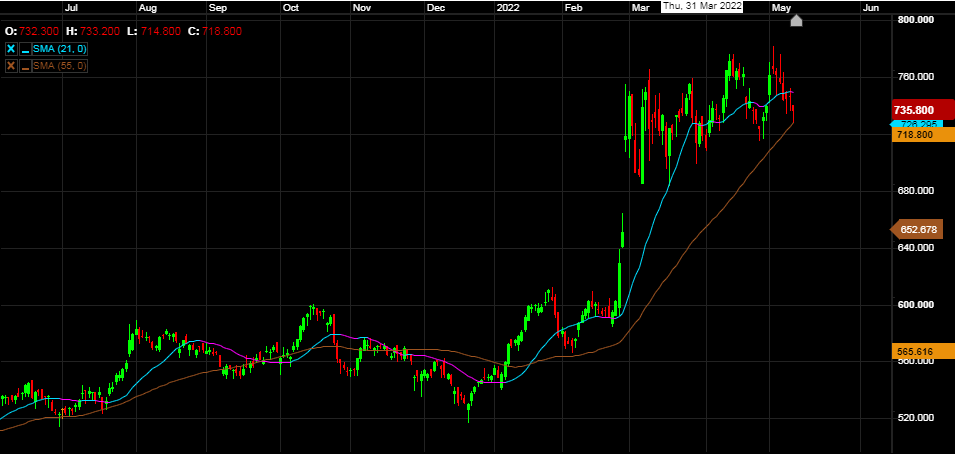
Rio Tinto
Rio Tinto is an Anglo-Australian multinational and one of the world's largest metals and mining corporations. The company was founded in 1873, when a multinational consortium of investors purchased a mine complex on the Rio Tinto, in Huelva, Spain from the Spanish government. Rio’s focus is mineral extraction however operations do expand into the refining of certain minerals, particularly bauxite and iron ore. Rio Tinto is a dual-listed company traded on both the London Stock Exchange and the Australian Securities Exchange. Additionally, American Depositary Shares of Rio Tinto's British branch are traded on the New York Stock Exchange giving it listings on a total of 3 major stock exchanges.
Rio’s main commodities are aluminium, copper, diamonds, gold, iron ore, and uranium as well as industrial minerals borates, titanium dioxide and salt.
Mining Stocks are also seen as a good inflationary hedge. As inflation rises so does the cost for the minerals they mine. Miners’ profits are directly tied to the price at which they can sell the metals they dig up and as the prices increase so does the profits. Of course, some metals will perform better than others so its always worth looking at a diversified mining company rather than a mining company tied to just one commodity.
Key Fundamentals
| Valuation | Balance Sheet | Income Statement |
| Market Capitalization85.984B | Current Ratio (MRQ)1.9349 | Basic EPS (FY)9.4771 |
| Enterprise Value/EBITDA (TTM)3.3630 | Debt to Equity Ratio (MRQ)0.2391 | Basic EPS (TTM)9.4620 |
| Total Shares Outstanding (MRQ)1.619B | Net Debt (MRQ)−1.297B | EPS Diluted (FY)9.4160 |
| Number of Employees49.345K | Total Debt (MRQ)9.99B | Net Income (FY)15.338B |
| Number of Shareholders35.102K | Total Assets (MRQ)75.969B | EBITDA (TTM)25.249B |
| Price to Earnings Ratio (TTM)5.4934 | Dividends | Gross Profit (FY)22.547B |
| Price to Revenue Ratio (TTM)1.8235 | Dividends Paid (FY)−11.166B | Last Year Revenue (FY)46.168B |
| Price to Book (FY)2.2002 | Dividend Yield Forward11.1865 | Total Revenue (FY)46.168B |
| Price to Sales (FY)1.8218 | Dividends per Share (FY)5.7756 | Free Cash Flow (TTM)13.981B |
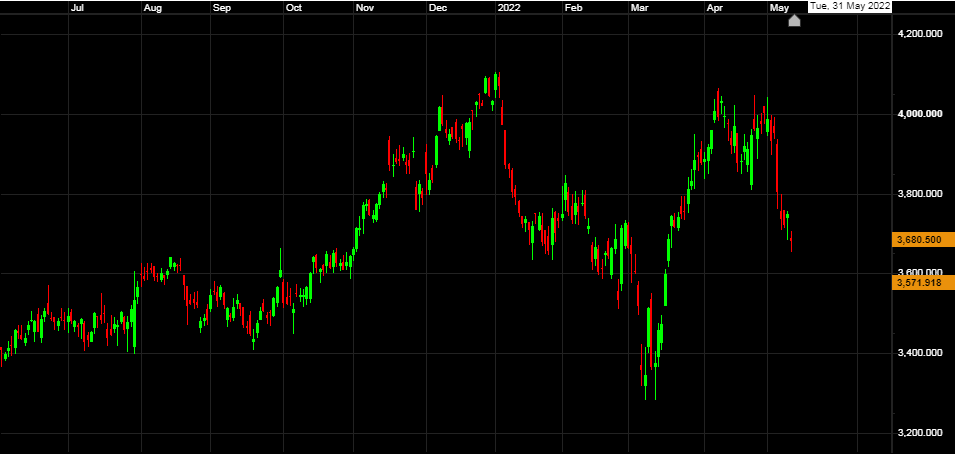
Diageo
Diageo is a British multi-national beverage alcohol company, with its headquarters in London. Diageo was formed in 1997 from the merger of Guinness Brewery and Grand Metropolitan. It now operates in more than 180 countries. It is a major distributor of spirits and the world's largest producer of Scotch whisky. Diageo has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. It has a secondary listing on the New York Stock Exchange. Diageo posted decent results in January, with net sales up 15.8% to £8bn and strong organic growth, despite currency fluctuations. Organic net sales were up 20%, while reported operating profits rose 22.5% to £2.7bn.
The range of products is almost as large as the countries they operate in and include various types of drink. Their portfolio includes most notably, the Scotch whisky brands , Johnnie Walker, Bell's, Black & White, Oban, Talisker, the leading vodka brand Smirnoff, the rum brand Captain Morgan. Their Liqueur brands include Baileys, Sheridan's and Pimm's. Their Tequila brands Don Julio, DeLeón and Casamigos. They also own the leading gin brands of Gordon's, Tanqueray, Gilbey's and Aviation Gin and of course the beers include Guinness, Tusker, Harp Lager, Kilkenny, Senator, Meta Abo and Smithwick's.
Diageo also owns a 34% stake in the Moet Hennessy drinks division of French luxury goods company LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE.
Key Fundamentals
| Valuation | Balance Sheet | Income Statement |
| Market Capitalization85.157B | Current Ratio (MRQ)1.5224 | Basic EPS (FY)1.1382 |
| Enterprise Value/EBITDA (TTM)22.5183 | Debt to Equity Ratio (MRQ)1.4872 | Basic EPS (TTM)1.3048 |
| Total Shares Outstanding (MRQ)2.319B | Net Debt (MRQ)12.031B | EPS Diluted (FY)1.1343 |
| Number of Employees27.783K | Total Debt (MRQ)13.877B | Net Income (FY)2.66B |
| Price to Earnings Ratio (TTM)28.5694 | Total Assets (MRQ)33.16B | EBITDA (TTM)4.683B |
| Price to Revenue Ratio (TTM)6.2882 | Dividends | Gross Profit (FY)7.735B |
| Price to Book (FY)12.5793 | Dividends Paid (FY)−1.646B | Last Year Revenue (FY)12.733B |
| Price to Sales (FY)6.8405 | Dividend Yield Forward1.9911 | Total Revenue (FY)12.733B |
| Dividends per Share (FY)0.7255 | Free Cash Flow (TTM)2.845B |
Hedging Your Portfolio
If current market conditions are causing concerns for your portfolio, then please feel free to watch our video on shorting the market below.
Dont forget to subscribe as well for all our content hot off the press. Market Guidance, Week Ahead Reviews, Special Reports and More.
About Atlantic Capital Markets
We are an independent UK based and regulated Multi-Asset broker. Offering our clients, the ability to trade using a range of products such as shares, CFD’s and options. Our range of services vary from a full advisory service for those that want an advisor by their side to the self-trade alert based account for those that want signals but be left to it.
Call us on 01872 229 000.
Disclaimer
We have provided this information for your general guidance only and it should not be considered as
investment advice. Atlantic Capital Markets will not be liable for any loss or damage caused by a reader’s
reliance on information provided by us. We make no claims or representations as to the accuracy or
completeness of any material contained in our guides. Atlantic Capital Markets is Authorised and Regulated
by the Financial Conduct Authority (No 764562).



